Internet of Things (IoT) devices have experienced remarkable growth over recent years. When companies explore the advantages of adopting IoT solutions, their worth becomes abundantly clear.
IoT devices can boost organizational efficiency by tracking and automating critical business processes like manufacturing, maintenance, and supply chain management. Further, the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices contribute to improved business information and analytics, providing customers with more tailored customer experiences.
As IoT is such an emerging technology, more companies that invest in it are outstripping their competition by effectively managing IoT devices and their data. To do this, robust data integration processes must be in place; otherwise, numerous barriers could be encountered when trying this new approach.
Here are key considerations you must consider when integrating IoT data.
- IoT devices give businesses unprecedented efficiency and insights that shape business operations and customer behavior. However, collecting all this IoT data can present its unique challenges and difficulties.
- An effective data integration plan is vital to successfully collecting and analyzing IoT data.
- Various solutions, including modern integration platforms, are available when formulating your plan to address issues related to data integration.
This article will outline businesses’ difficulties when integrating IoT Data, along with potential solutions.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things is a device connected to collect data and transfer it to a network without human intervention.
“Things” refers to the built-for-purpose nature of IoT devices. IoT data can originate from cameras or sensors connected to embedded systems, equipment such as gauges, scales, or any other smart object.
Companies use IoT to gather more information about their operations. The data collected provides a better understanding of operations efficiency, customer behaviors and expectations, and decision-making processes. IoT technology is also employed to automate various business functions.
Explore More: Introducing IoT Data Collection Platform Development to Revolutionize the Future
Key Challenge in Implementing IoT Systems 2024
The process of developing IoT solutions has many challenges. Solving these challenges is essential since the IoT market expands as more devices are installed, which could lead to security breaches.

>Coverage
The network connection is crucial for an IoT operation. Without it, an IoT device will disappear from the market and significantly impact your operation or essential services.
Finding the ideal network to run your business is a crucial component of due diligence since some network choices will severely restrict the locations where IoT devices can be placed.
Some, for instance, may opt to utilize Wi-Fi for IoT connectivity; however, this could restrict the range of operation since devices will always have to be within a certain distance of the router hosting them.
Locations that have a third site owner or pose problems due to security issues or are complex and challenging for security to control credentials.
Wi-Fi is essential, but the majority of Pure IoT or hybrid devices require access to Wi-Fi because of manufacturing constraints or end-user requirements.
For instance, remote-managed printers, local EV charge points, or payment systems usually require Wi-Fi as a primary or second connection.
This could cause problems due to geographical location, cost limitations, or required cases. For instance, the extra cost of a 5G or 4G modem is deemed to be prohibitive to the end-user consumer.
In the absence of the right infrastructure, no matter what mix of connectivity is required, you’ll have to either equip all devices using a backup solution or invest in a reliable router and security for your network to ensure that dispersed devices are connected.
>Scalability
With more than 15.14 billion IoT devices worldwide, it’s not uncommon for an IoT Development Company to deploy thousands or hundreds of thousands of IoT devices worldwide.
Every device will likely have its unique management platform that communicates with the firmware that it is running connectivity technology and the global systems for support. These systems are private, making scaling mission-critical IoT operations challenging.
The ability to scale can be more challenging if your product has to be fundamentally altered to accommodate the latest connectivity options. This decision requires consideration at the device or system design phase.
This IoT issue also relates to cellular IoT operations since Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) can offer different roaming capabilities and support (or support) across various regions.
Operators can have various types of contractual agreements that could result in significant differences in roaming costs and other oddities.
A growing number of countries have banned permanent roaming, which implies that local profiles must be made available via in-the-air (OTA) for these types of restricted access zones in the country (I.e., Turkey & Brazil).
Due to the roaming ban, problems can arise when you expand your business across different countries or within specific areas with permanent roaming restrictions.
This concerns devices that are anticipated to travel internationally within areas with such regions, i.e., logistics transportation, vehicles, and post-market Telematics.
Explore More: AI in the Air: How AI is Reshaping the Aviation Industry
>IoT Security
IoT security issues are not new. Since the IoT was first made available, devices have been targeted by cyberattacks. Take, for instance, the famous Mirai Botnet case, which affected Linux devices, including routers and cameras.
If a Custom IoT Development is compromised, the information it gathers could be obtained by a third party without the user’s consent. This could result in dire consequences, not just for businesses but also for consumers.
For instance, if a person or organization attempted to hack an IoT smart home/building/router system, they might gain access to private data.
It could also include sensitive personal or commercial details, like security credentials, bank account information, email addresses of users, and home addresses.
IoT devices and routers must be configured and connected for secure network access and managed only by systems with top-of-the-line security solutions, methodologies, and procedures.
Incorporating authentication, encryption, or tunneling security protocols into IoT devices will help protect them from cyber-attacks. However, most IoT devices are limited in power source, and including these security protocols could significantly make it more difficult to implement technological resources, the skills required to create and support these protocols, and the power requirements of simple transmissions.
As a result, many devices still need to integrate these features into them.
Implementing on a large scale or providing complicated connectivity solutions that involve multiple devices interconnected with local router infrastructure makes these aspects crucial.
This is the most common situation when implementing branch or retail systems, and cameras are a must for security or privacy.
As technology and methods evolve, new IoT security threats are expected to be revealed. If you do not update your devices, you’ll discover that they are becoming more vulnerable to attack.
This is why the law of England now requires the connectivity of EV Charge Points, which means that crucial security and safety updates can be implemented quickly and safely.
>Limited Battery Life
In the last IoT challenge, many IoT equipment had a short battery life. The batteries are usually tricky to recharge because they are placed on sites not owned by third parties or in remote areas. This makes it challenging to keep them running and functional.
This becomes a bigger problem when devices transfer large amounts of data through wireless connections or require regular software updates.
However, larger batteries limit the places devices can be put in or their reliability and usage, limiting their applications and diminishing their chances of effective scale.
If the battery were larger and utilized for predictive maintenance purposes in this scenario, it could make the device more challenging to implement in a plant or vehicle, making it more susceptible to the risk of hot temperatures or impact. Wearable devices for remote care or lone worker applications can become costly and unusable.
Another important aspect is that devices will spend most of their lives in remote locations with access to a power source. An incorrect network can lead to connectivity issues and reduce lifespan; reducing the device’s lifespan infrastructure is vital for every IoT operation. However, hosting multiple devices on the same network could create delays, decreased performance, and a higher latency rate.
This issue is compounded when dealing with critical applications like factory automation, sophisticated retail systems, and the medical Internet of Things (IoT). A network failure can have serious consequences, making it challenging for companies to ensure essential services.
Explore More: All You Need To Know About The Internet Of Everything (IoE)
>Limited Bandwidth Availability
The volume of information IoT devices generate is huge when viewed in the context of scale and will only increase as their capabilities grow. In reality, IoT devices are expected to style=”font-weight: 400;”>generate around 80 Zettabytes of data by 2025. That’s 45.7 percent of the worldwide data. (erp.today, 2024)
One of the most significant IoT-Wearable Connectivity Development issues they face is the limited bandwidth they have access to due to their deployment in remote areas.
This could make it difficult and costly to send all the data collected. As in any IoT operation, servers have to sort and analyze the ever-growing quantities of data it’s confronted with quickly.
However, if there are excessive IoT devices and users within the same distance, it could cause congestion in networks, which can result in slow response times and lower performance.
>Remote Access
There are a variety of IoT connectivity issues that affect devices that are deployed in remote areas. It could be due to limited access to sites and third-party ownership for devices or the inability to permit downtime during updates due to their security or critical nature.
Many of these devices may not be able to access power or require special forms of connectivity because of their distance or propagation requirements.
For a device to function in this kind of environment, Many organizations rely on technical personnel who visit the location to help with the setup. This can be costly, time-consuming, and logistically challenging, particularly if the facility is located in a difficult-to-access location or is located out of the country.
Remote access options significantly reduce the cost of maintenance and support. These capabilities are increasingly incorporating the possibility of installing local routers that can manage important devices and services independently and remotely in these kinds of locations.
>Interoperability
One of the most essential IoT business issues that many service providers and even you might face is ensuring that your IoT products are in sync with one another and your business applications.
To adapt to any brand-new software or hardware, you may have to implement changes in a chain to ensure that your IoT operation functions in line with the others.
Although this isn’t the case for all IoT operations, a different issue to consider is whether the technology utilized to create the IoT solution is open source, proprietary, or compliant with major standards like ISO, ETSI, or the GSMA. ISO,
Explore More: Top Trends in Agritech Software Development in 2024
>ETSI or the GSMA
Without a designated regulatory body, the quality of software could be different because there is no universal standard that has to be followed, or, in fact, it could make it more difficult for developers to develop partners in integrating essential services.
Integrating new technology or functionality from various vendors or setting up your IoT operations in a different area can be challenging.
>Maintenance
The final IoT business challenge on our list is maintaining IoT devices. Since these devices must regularly be connected to the Internet, they need continuous maintenance to ensure their security and performance. In the most extreme cases, this could require manually updating every device with the most current patches and improvements to the software.
It can be costly and time-consuming, precisely when many devices are spread across multiple geographical locations and regions.
The device’s connectivity also requires monitoring. The protection of mobile networks is a crucial aspect of a device’s function and requires that the performance of devices be tracked and adjusted to ensure that they don’t frequently and often send signals in a jumble.
This type of signaling storm could be caused by devices that cannot connect for a brief period or when they fail. This is a severe issue for mobile operators. Devices malfunctioning or failing to utilize algorithms to distribute traffic may shut off a network.
With the ever-growing expansion and use of IoT devices over the past few years, older devices begin to resemble junk and, if they are not turned off, could cause constant headaches.
Many mobile operators are making kill commands to eliminate problematic older, outdated, inactive, or obsolete devices that are deemed to be a nuisance or threatening to the network.
Exploring Major Vulnerabilities in IoT Devices
Knowing about the vulnerabilities of IoT devices is increasingly vital as IoT devices continue to improve.
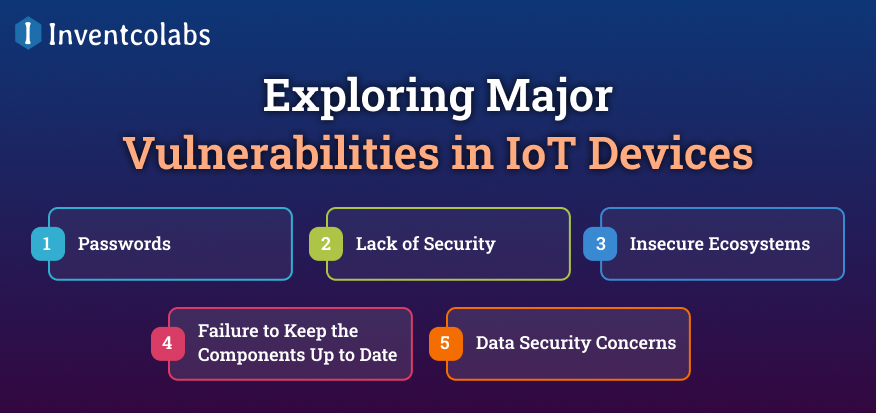
>Passwords-
That are simple to guess could lead to unauthorized access to industrial equipment.
>Lack of Security-
For networks, referred to as Man-in-the-Middle Attacks (MITM), is targeted at creating vulnerabilities between the communication protocol and the services that run within IoT devices.
>Insecure Ecosystems-
Components like the backend, web API cloud, and mobile interfaces should be protected by safe and reliable encryption methods.
>Failure to Keep the Components Up to Date-
With the latest software requirements or systems that are not up-to-date could harm the whole IoT ecosystem.
>Data Security Concerns-
The data stored must be in compliance with privacy laws (GDPR or CCPA) to avoid legal penalties.
Importance of Encryption in Securing IoT Data
It is a key element in protecting IoT data due to the privacy issues that exist in IoT and the reality that IoT devices can be hacked without security and privacy protections implemented.
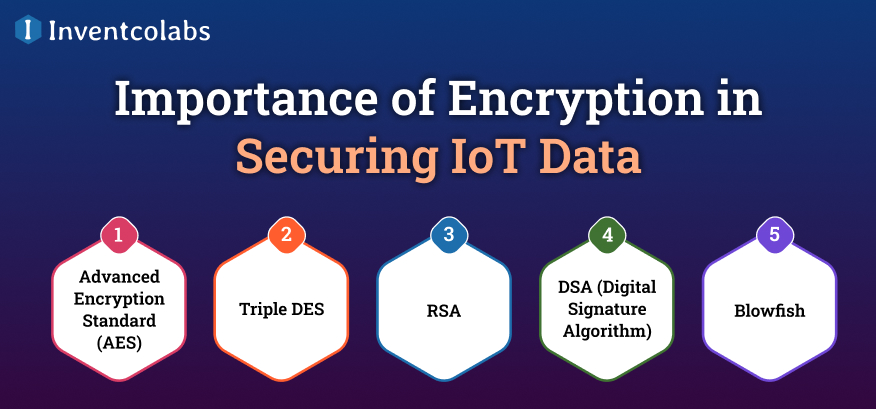
IoT Development Company uses synchronous (singular cryptographic key) and Asynchronous methods (multiple keys) to protect information. The most widely used techniques include:
>Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)-
AES is an encryption algorithm used by security agencies and other organizations worldwide. It is easy to apply and implement across a variety of IoT security fields.
>Triple DES-
DES is the successor to the DES algorithm (which is no longer in use). It is often used in payment systems and FinTech solutions.
>RSA-
It is commonly used in SSL/TLS certifications, email encryption, and cryptocurrencies.
>DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm)-
It was built in the late 1990s by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). It allows you to create two digital signatures that allow the recipient to verify the sender’s authenticity.
>Blowfish-
Blowfish is free and can be used to safeguard online transactions and user password security.
Explore More: The Comprehensive Guide to Fleet Management Software USA 2024
Conclusion
The world of industrial IoT is changing rapidly, and billions of IoT devices are being installed in diverse industrial fields, including healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. As IoT solutions become more commonplace, new issues arise regarding security practices and audits to ensure that IoT devices are secure. IoT manufacturers need to prioritize safety and develop appropriate strategies to protect their current and new IoT devices.
This is achievable through tested solutions and partners that have a history of delivering successful projects. The benefits include:
- The ability to access talent.
- Reduced time to market.
- The capacity to consult about IoT software deployment.
A thorough planning of all activities and market research is an essential step that should be addressed in the long run. IoT projects require awareness of the whole IoT infrastructure and its risks.




