Like any other technology, the internet ecosystem is constantly evolving to meet society’s rising expectations. And consumers should stay aware of the Internet’s future as that will help avoid digital whiplash resulting from the changes that Web 3.0 brings. But what exactly is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is a third-gen of the Internet facilitating many new capabilities, and the most important is the “decentralization of internet content regulation.” This technology is creating the same kind of stir as created by Blockchain technology and has similarly left people perplexed about what it is about.
Meanwhile, to offer a simple understanding, there have been two versions of internet computing. Each has gradually added more and more online services, thus opening up new digital doors. In the case of Web 1.0, it was the first internet phase that displayed information. Still, it had its limitations in terms of capability, inept at navigating, and didn’t offer many options to monetize content. Then Web 2.0 was an improved version that categorizes information on websites, enabling data to freely flow from the site owner to user, providing tools for content creation. And the latest version of Web 3.0, upon its arrival, has caught the attention of the likes of VC firms, tech companies, and cryptocurrency enthusiasts.
What is Web 3.0?
Also known as web3, Web 3.0 is the third iteration of Internet interconnecting data in a decentralized manner delivering a faster and much more personalized user experience. Web 3.0 is built using Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, and Semantic web, and it uses a blockchain security system to keep the information safe & secure. Its three key characteristics are openness, decentralization, and incredible user utility.
The reason for using the semantic web is that it allows understanding and interpretation of the concept and context of data. Thus, as the end-users initiate a search to find the answers, Web 3.0 presents the most accurate result. Here the data are connected in a decentralized manner, mainly in a blockchain, and this is why Web 3.0 is highly transformative from earlier Web 2.0 centralized architecture. Web 3.0 is way more scalable, secure and offers better privacy to its users.
Biggies like Microsoft, Facebook, and Google immensely benefit and earn a great deal of money using user data. People have been giving away their valuable data with little or often no compensation from the companies collecting this data and benefiting from it. However, Web 3.0 will allow people to be compensated for their time and data, and people will be paid for the information they share. Web 3.0 enables people to sell their data to advertisers while retaining ownership & data privacy.
Hence, the users will be able to retain data privacy and ownership while also making it available for the companies to target them. Additionally, Web 3.0 also allows websites and apps to use data more meaningfully and tailor information to each user.
What are the key features of Web 3.0?

The key features of Web 3.0 are:
-
Ubiquitous:
With Web 3.0, the Internet will be available to everyone at all times and from anywhere. There will be a time when Internet-connected devices will not be limited to smartphones and computers, as was the case with Web 2.0. Owing to the Internet of Things (IoT), this technology will allow the development of many new kinds of intelligent gadgets. -
Permissionless:
In Web 3.0, every one, also consisting of the users & providers, can engage without requiring permission from a governing organization. -
Trustless Data:
With Web 3.0, the users get the freedom to publicly & privately interact, with no intermediary exposure to risks. This results in trustless data. -
Openness:
Web 3.0 is open in a way as it is made with an open-source software created by an open & available community of developers, and it is capable of the full view of the public.
How Web 3.0 is different from Web 1.0 and Web 2.0?
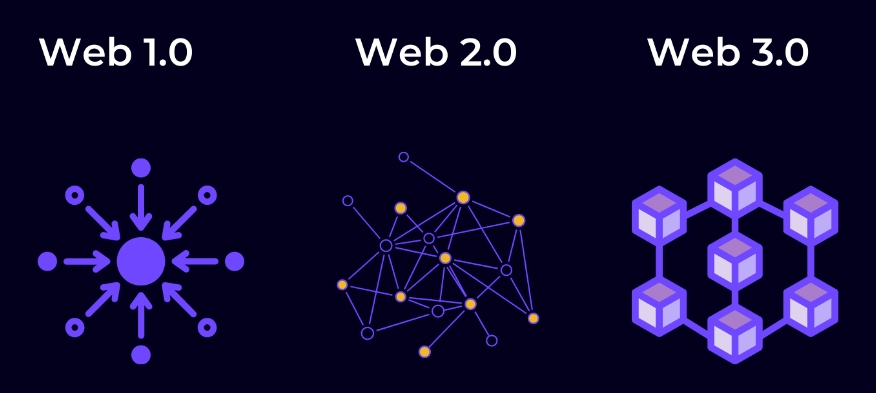
To make the understanding simple:
- Web 1.0 is a read-only web that allows people to read information written on the website.
- Web 2.0 is a read-write web that enables people to read and write content on applications and websites.
- Web 3.0 is a read-write-interact web that Artificial Intelligence powers, and it allows people to write, read, and interact with the content, including 3D graphics on apps and websites.
In 2006, the term Web 3.0 was first coined by John Markoff, a reporter for The New York Times. We can say that Web 3.0 is a return to Berners-Lee’s original Semantic Web concept, requiring no central authority approval and with no existing central controlling node.
What technologies are use to build Web 3.0?

The earlier Web 2.0 was mainly driven by the introduction of social, cloud, and mobile technologies, whereas Web 3.0 is powered by new layers of technology innovation, which are:
Decentralization:
With decentralized data networks, several data generators can sell/trade their data without losing ownership, risking privacy, or relying on intermediaries. Resultantly, decentralized data networks will have a long list of data providers in the growing data economy. For instance, as you log in to an app via email & password, or when you like a video, or ask Alexa a question, all of these activities are tracked and monitored by the tech giants like Facebook and Google to target their advertisements effectively.
However, in Web 3.0, the data is decentralized; hence users own the data. With decentralized data networks, data generators can sell and trade their data without losing ownership, risking privacy, or relying on intermediaries. With Internet Identity, it is possible to log in without getting tracked securely.
Blockchain:
Blockchain is the foundation of Web 3.0 as it is pivotal in redefining data structures in the backend of the semantic web. Blockchain is a decentralized data machine deploying intelligent contracts, which define the logic of an app for Web 3.0. Hence anyone willing to create a blockchain app must deploy their app code on the shared state machine.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
AI and ML algorithms have advanced, making valuable and, at times, life-saving acts and predictions. When the apps are built on the top of decentralized data structures providing access to a lot of data desired by present-day tech titans, they extend much beyond the targeted advertising into areas like Climate modeling, Medication Creation, and Precision Materials. Even though Web 2.0 has similar abilities, it is still primarily human-based, enabling corrupt behaviors, like biased product evaluations, human errors, rigged ratings, etc.
For instance, with Internet review services like Trustpilot, customers can leave their feedback on any products or services. However, some firms might be paying a large group of people to write exceptional evaluations for their products/services. Hence, the Internet needs Artificial Intelligence to learn to discriminate between genuine and fake to deliver accurate data. Post the Gamestop trading incident, Google’s AI system recently erased around 100,000 negative ratings on the Robinhood app from Play Store after it detected attempts at rating manipulations were meant to downvote the app intentionally. As AI is integrated into Web 3.0, it will allow blogs and other online platforms to filter through the data and personalize it to suit each user’s preferences.
Edge Computing:
The big shift with Web 3.0 is moving the data center out of the edge (i.e., edge computing) and straight into our hands at times. The data centers are accompanied by a range of advanced computing resources distributed among laptops, phones, sensors, cars, and appliances, producing and consuming 160 times more in 2025 than in 2010.
Understanding the working of Web 3.0
The main idea for Web 3.0 is to make Internet searches much faster, easier, and more efficient so it can efficiently process even the most complex search sentences quickly. In the Web 2.0 app, users had to interact with its front end that communicates to its back end, ultimately communicating with the database. Here the entire code is hosted on the centralized servers that are sent to the users via an Internet browser.
However, in the case of Web 3.0, it neither has centralized databases to store the app state nor has a centralized web server where backend logic resides. Instead, it has a blockchain building apps on a decentralized state machine, and the anonymous nodes maintain it on the web. The logic of the apps is defined in smart contracts written by developers, and they are deployed onto a decentralized state machine. People keen on building blockchain apps can deploy their code on this shared state machine, and here the front-end is almost the same as in Web 2.0.
What are the benefits of Web 3.0?
With Web 3.0, the web world will become way more intelligent, transparent, and secure, leading to proficient browsing and successful machine-human interaction. The main benefits of Web 3.0 are: 
- On the Web 3.0 network, users are not required to create individual personal profiles for different platforms. With Web 3.0, a single platform works on any platform, and the users have complete ownership of any information.
- As with Web 3.0, the blockchain network is accessible to everyone, so the users can create their addresses or interact with the network. Users are not restricted based on their gender, geographical location, age, or sociological factors on this network.
- With Web 3.0, the data is easily accessible anywhere and on any device. Here, the idea is to increase data collection and make it accessible to users worldwide by enabling smartphones and other connected devices to access the data on the computer when synced easily.
- Web 3.0 is transparent. With web 3.0, irrespective of the blockchain platform used by the end-users, it will be easier to track their data and inspect the code behind the platform. This eliminates user dependency on an organization that has developed the platform.
- Web 3.0 offers decentralized data storage, which ensures that the data is easily accessible to the users in any circumstance. Here the users get any backups, which benefits them even when there are server failures.
- Web 3.0 offers Data Privacy & control. It allows the end-users to get a significant advantage of data encryption, protecting their information from disclosure. Hence, big firms like Apple and Google won’t be able to use people’s data without their permission.
What importance Web 3.0 will hold in the future?
Among the many reasons why Web 3.0 will be crucial in the coming years, a few are: 
- It offers peer-to-peer connectivity, which allows businesses, humans, and machines to share more data while maintaining security and privacy.
- Web 3.0 can be helpful in disintermediating businesses, removing rent-seeking intermediaries, and giving this value to customers & providers in a network directly. The network users work together to address the previous uncontrollable problems by mutual ownership & governance of the new decentralized intelligence configurations.
- A constant demand has been registered for humanized digital search assistants that are way more ubiquitous, intelligent, and powered by semantics, Blockchain, and AI. This demand will only increase in the future.
- Web 3.0 will be critical in the future as most users will continue prioritizing tailored and personalized browsing experiences on the web.
- Web 3.0 endeavors at making the Internet a diverse source, so any leaks, hackers, and reliance on centralized repositories are avoided.
- The knowledge of the next Internet generation can be further helpful in lessening the dependency on individual platforms, hence future proofing entrepreneurial & investment activity.
Conclusion:
The Internet is changing many people’s lives for the better, and Web 3.0 is the next big step in Internet evolution. It is helpful as it enables businesses to streamline their operations by letting go of the mediators and connecting directly with the computers, thus allowing efficient and effective communication and collaboration between the partners, employees, and customers.
At InventColabs, we are an ecommerce development and mobile app development company providing services in the area of Blockchain, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, etc. You can connect with us and hire a dedicated developer to assist with your web or mobile projects.
FAQs
Q. What is Web 3.0, and how long will it take for it to be fully implemented?
Ans. Web 3.0 is a third-generation internet service focusing on innovative, data-driven, and services-based design. For the second part of this question, several tools essential for web3 are developed, and some are already in use. As the concept for Web 3.0 is complex with some technical issues, it will take some time to transition from the present Web 2.0 to be implemented fully.
Q. What is a Decentralized Web App?
Ans. Instead of running on a single server, dApps use a peer-to-peer network or a blockchain to execute. Decentralized web apps are an attempt at democratizing the Internet again.
Q. Why is it also called Semantic Web?
Ans. It is also known as Semantic Web as here the web apps can recognize, perceive, understand, and respond as per user requirements.
Q. What are the technologies used by Web 3.0?
Ans. It uses technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, Smart Contracts, and Immersive Graphics.
Q. Is Web 3.0 built on Blockchain?
Ans.Blockchain technology is the main foundation for Web 3.0, IoT, ML, AI, and decentralized data storage.
Q. Is Web 3.0 similar to Blockchain?
Ans. No, it is not. Even though Web 3.0 uses Blockchains, it also uses other technologies, and Blockchain has many use cases like NFTs and cryptocurrencies.



